| Cart Empty |
Herbals Products For Daily Life
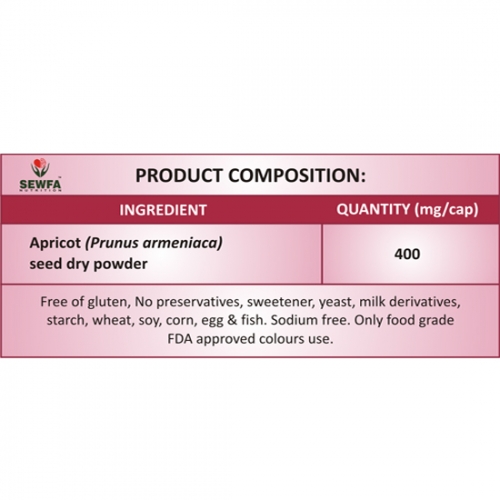
About the Product:

RECOMMENDED
DOSE:
Take 1 capsule twice daily preferably with meal or as directed by your
healthcare professional.

GOOD FOR WEIGHT MANAGEMENT
SUPPORTS TO HEART, BRAIN, BONE & EYE
A plant –based Omega 3-6-9 Fatty acids
ACTION OF ALPHA LINOLENIC ACID (ALA) FROM FLEX SEEDS:
- ALA
supports heart health and helps toprevent heart
attacks, lowers high blood pressure, cholesterol, and reverse “hardening of the
blood vessels” (atherosclerosis).
- It
creates and maintains healthy serotonin levels.
- ALA
Increase immune system health & energy level
- ALA supports eye health by helping to maintain photoreceptor
membrane integrity and ensuring optimal production of vision through light
transmission (1).
- It improves cognition health; lowers stroke risk & cerebral
blood flow.
ACTION OF CONJUGATED LINOLENIC ACID (CLA) FROM SAFFLOWER:
- CLA regulates cellular activity
& inhibits the growth of cancer cells.
- It reduces adiposity (fat) &inhibits
lipoprotein lipase which is involved in the storage of fat into fat cells (2).
- CLA is beneficial for lowering joints pain, inflammation and morning stiffness.
- It
effective to reduces rheumatoid arthritis as
well as improves bone mass.
- In addition to the antioxidant,
anti-inflammatory and insulin-sensitizing actions of CLA, it can help prevent
muscle loss and weakness associated with aging and disease. This is one of the
key reasons CLA is a favourite supplement of both athletes and body builders.
- CLA is good for weight
management.
ACTION OF GAMMA LINOLEIC ACID (GLA) FROM BORAGE:
- GLA is used to produce prostaglandins
(hormone-like substances that help to regulate the immune system (3).
- It raises metabolism by making brown fat
(adipose tissue) in the body. It potentiates fat loss
and increases energy.
- GLA supports hormones related PMS and Menopause.
- It also improves cell
sensitivity to insulin, helping to reduce chances of developing diabetes, heart
disease and excess body fat. GLA with your meals to increase metabolic rate
&its absorption.
RECOMMENDED
DOSE:
Take 1 capsule twice daily preferably with meal or as directed by your
healthcare professional.
PACK SIZE: 60 soft gel capsules
References:
- Querques G., Forte R. and Souied EH. Retina and omega-3. Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism. 2011; PMID: 22175009.
- Kennedy A., Martinez K., Schmidt S., Mandrup S., LaPoint K and Mciltosh M. Antiobesity mechanisms of action of conjugated linoleic acid. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2010; 21(3): 171–179.
- Harbige LS. Fatty acids, the immune response, and autoimmunity: a question of n-6 essentiality and the balance between n-6 and n-3. Lipids. 2003; 38(4):323-41.
Frequently Bought Together
Garcinia Extract
425
Triphala Extract
425
Turmeric
888
Wheat Grass
444
Moringa Extract
666
Sewfa Arthofit
555
Sewfa Digest
333
Sewfa Diabcare
333
Multivitamins
555
Omega 3
1,222
Similar Products
Sewfa Arthofit
555
Sewfa Digest
333
Sewfa Diabcare
333
Multivitamins
555
Omega 3
1,222
Omega 3-6-9
1,111
Testone 5
777